- Published on 27-Apr-2022
- 0 Likes
- 0 Comments
- 372 Times Read
Heart disease is a global problem that affects both rich and poor countries. Tachycardia is one of many medical health conditions that relate to the heart.
In a normal adult, the average heart beat is sixty to one hundred beats per minute. A heart beating above one hundred beats per minute is called Tachycardia (the heart is pumping too fast). This condition can occur naturally, such as when you are exercising resulting in the heart rate being accelerated Tachycardia can also cause life threatening and serious heart problems. There are a variety of ways in which the heart normally increases its tempo. These include exercise, fever or if the person is anxious or excited.
Problems with the heart that can cause tachycardia are varied.
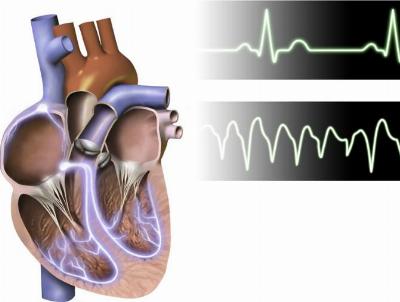
Atrial Fibrillation is an abnormal pattern where the right and left atria (upper heart chambers) are contracting irregularly thus making the heart beat faster.
Mistral Valve Prolapse is when one of the valves in the heart has a mid deformity, thus causing a fast heart rate.
Ventricullar fibrillation is the most serious type of tachycardia. This is the most serious type of tachycardia. The heart beats in an irregular rhythm and very fast. The ventricles contract (squeezing) chaotically, that prevents the heart from pumping. When this happens, the blood circulation stops. Sometimes the episodes are brief and subside really quickly. The majority of times, ventricular fibrillation require immediate medical treatment to prevent any the brain from being damaged and preventing death.
The main symptom of any type of Tachycardia is a fast heartbeat. Other symptoms requiring medical treatment may include lightheadedness, fainting, nausea, cold sweat, shortness of breath and chest pain.
These symptoms can be caused by any type of tachycardia, ranging from mild to severe. Please contact your doctor if you are having any of these other symptoms in addition to the fast heartbeat.



0 Comments