- Published on 09-Mar-2022
- 0 Likes
- 0 Comments
- 455 Times Read
Hepatocellular carcinoma commonly known as liver cancer is a deadly cancer. It will kill almost all patients who have it within a year. The World Health Organization estimated approximately four hundred thirty thousand new cases of liver cancer worldwide and a similar number of patients died as a result of the disease. Most common areas of the world with high rate of people being affected by the disease are the sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia.
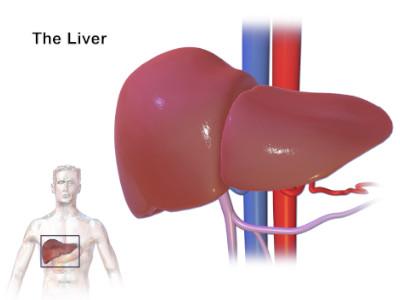
The liver is the largest organ in the body, which is found behind the ribs on the right side of the abdomen and it has two parts: the right lobe and the smaller left lobe. It has many important functions that keep a person healthy; it removes harmful materials from the blood, it makes enzymes and bile that help us digest food, and it also converts food into substances needed for life and growth. The liver gets its supply of blood from two vessels, the hepatic portal vein where most blood comes from, and the rest comes from the hepatic artery.
Hepatic tumors are tumors or growths on or in the liver, which can be benign or malignant (cancerous). Tumors of the liver occur when there is an inaccuracy in the normal regulation of growth of any cells in the liver, including the liver cells themselves (hepatocyte), the bile duct, or the blood vessels within the liver.
Initial symptoms of liver cancer are unpredictable. In countries where this disease is very common, generally the cancer is discovered at a very advanced stage of the disease because of several reasons; one of them being the areas where there is high frequency of the disease are usually developing countries and access to healthcare is limited, another is screening examinations for patients at risk for developing the cancer are not available in these areas. To add up to these, patients from these regions actually have more aggressive liver cancer diseases therefore reaching the advanced stage more rapidly. Symptoms of this disease include pain in the upper abdomen on the right side (the pain may extend to the back and shoulder), swollen abdomen (bloating), weight loss, loss of appetite and feelings of fullness, weakness or feeling very tired, nausea and vomiting, yellow skin and eyes, dark urine from jaundice, and fever.
The best way to prevent liver cancer is avoiding the risk factors that are linked with it. Keeping away from the excessive use of alcohol and quitting smoking can reduce the risk of liver cancer. Preventing and treating HBV and HCV infections is also important. In other parts of the world, changing the way that foods are stored and processed can decrease the risk of aflatoxin exposure. Proper treatment of water can reduce the risk of arsenic in drinking water. Right treatment of inherited diseases associated with cirrhosis and liver cancer can reduce the risk of developing either of the disease. Although the risk of liver cancer can never be diminished to zero, it can be significantly reduced by avoiding known risk factors.



0 Comments